|
|
|||||
![]()
|
The greenhouse effect |
|
|
The
publication of the second report about the state of knowledge on climatic
changes (SAR, Second Assesment Report) of IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel On
Climate Change) is an important step in the study of greenhouse effect. The
SAR collects the work of more than two thousand scientists all over the world
and it holds the researches of hundreds more. Published in four volumes of
2000 pages, itís rich in scientific data and researches; for the first time
the experts all over the world confirm the influence of the man on climate. The
IPCC declares that " The projections, included in this report, point out
clearly that the next climatic changes will be dominated by the influence of
man, unless the composition of the atmosphere becomes stable".
|
|
|
The
problem Human
activity is going to increase the concentration of the greenhouse gases in
the atmosphere, which trap the solar heat warming the planetís surface, the
IPCC foresees that considering a moderate percentage of the development of
human activity, the concentration of the greenhouse gases will increase so
much to cause in the next century a rise in average temperature of about
1,5-4 įC (this means that in some places the temperature might drop
temporarily and in other places it might raise of many degrees).As regards to
the last century the temperature of the earthly surface had already raised of
0,3-0,6 įC . |
|
|
And as
the climate will change, the planet will react in different ways according to
the different areas, it will either accelerate the heating process or
mitigate it. The critical factors include the heating effect of the clouds,
of the forests, of the icebergs and of the ocean currents, the
interconnection among such factors is still difficult to foresee; this
scientific gap explains the large margins of error concerning the present
forecasts.
|
|
|
The
greenhouse gases Carbon
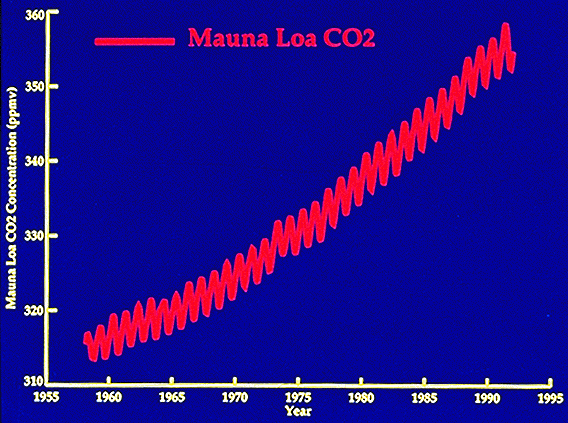
dioxide, methane, protoxide of azote, chlorinefluorinecarbides, ozone. As to
200 years ago the present concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) of 358 parts
per million is higher than 30% and itís responsible for 70% of the greenhouse
effect, itís the combustion of petroleum, carbon, gas, firewood and
deforestation which causes the discharge of CO2. A factor that has not been
much studied is the incidence of CO2 coming from the cultivated grounds, in
fact the grounds hold in large quantities organic |
|
|
substance
prevalently in the form of humus. It has a low index of mineralization
(transformation of the organic substance by means of the oxygen and the
enzymes in the primary components, water and mineral salts) equivalent to
1-3% annually, but it may be much higher if wrong agricultural usages are
practised that are very diffuse (frequent and/or deep cultivations of the
ground, leaving the soil exposed from the vegetable covering especially in
summer, burning residual products of the cultivations, ecc.). So there is the
real possibility that also the cultivated grounds help in the clear discharge
of CO2 in a significant way. The scientists havenít yet been able to describe
an exact balance of the carbon, but they have valued the quantity at 5,5
thousand millions of tons of CO2 discharged by the combustion to which 1,6
thousand millions of tons more are added, caused by deforestation and by
other uses of the ground at the Tropics. Then out of 7,1 millions tons
annually, 3,3 remain in the atmosphere, 2 are absorbed by the oceans and 1,8
seems to be utilized by the not tropic forests of the northern hemisphere. But
this process will not last a long time (see forests). The methane in the
atmosphere has increased by 145% exercising a greenhouse effect equivalent to
the third of that concerning CO2 that is 23%. The reasons of this rise are
less known, among them there can be the Ruminantia-breedings (whose digestive
systems yield methane), the rice-fields, the hoisting and the use of methane.
Today the levels of methane rise at a half speed in comparison to 20 years
ago, the reasons of this phenomenon arenít clear. All the other greenhouse
gases contribute for the remaining 7%, the protoxide of azote is emitted by
some agricultural activities, the ozone in the low atmosphere is produced by
the reactions among the polluting agents present in the atmosphere, the
chlorinefluorinecarbides produced by industry, through the protocol of
Montreal, signed in the 1987, ought to reduce this amount in the next years. |
|
![]()
|
|
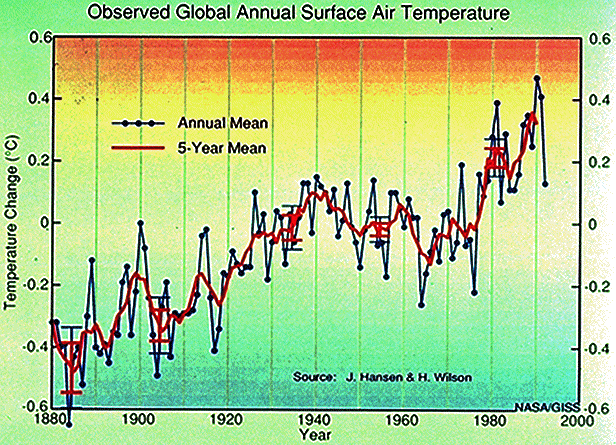
The
intensification of greenhouse effect has been in progress for over a hundred
years Since
1860 in the greater part of the globe the temperature of the earthly surface
has been raising of 0,3-0,6 įC, this happened especially from 1910 to 1940
and after 1970, besides most of the warmest years in the century have
concentrated in the last 15 years. The new data obtained from the core boring
of the polar ices, show that the rise of heating in the last 100 years has
been the most rapid one for the past 10.000 years. The sea-level has risen of
10-25 cm.and the rise of temperature doesnít concern only the surface but
itís reaching greater depths; the IPCC relates some recent studies which
notice a rise of temperature in the last 20 years of 0,3 įC in the Indian
Ocean as deep as 800 metres and similar ones in some areas of the Pacific
Ocean. The temperature of the continents has raised especially at the
temperate latitudes in the northern hemisphere, besides the night temperature
has raised in wide areas particularly, for example in the north-east area of
the United States in the last 30 years, it has been calculated that frosty
season has been 11 days shorter owing to warmer nights. The hydrological
cycle has changed too, in all the northern hemisphere since 1988 the snow
level has been below the average considerably and the spring thawing of snows
has began causing inundations in Canada and California. In many northern
countries the lakes and the rivers freeze 1-3 weeks later and they thaw out
earlier than average; most ices of the Alps have been reduced considerably. Studies
conducted about sporting salmon fishing in the Sacramento river have pointed
out a reduction of 23% of the population owing to the rise of the
temperature. Since 1950 the atmosphere which overhangs the oceans has
gradually become more overcast, at the Tropics the steam above the oceans has
been increasing too and since 1973 storms have been more frequent, instead on
a large area of the tropical and sub-tropical regions from Africa to
Indonesia, the rains have diminished since the 60ís.Since 1989 El Nino
(expansion of a superficial warm current of the Southern Pacific Ocean) has
had extreme manifestations periodically, a sudden rise of storms has been
registered in the northern area of the Atlantic Ocean and in some tropical
areas there has been an exceptional drop of rains. The climate looks like it
is being characterized more frequently by extreme meteorological
manifestations. |
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
![]()