Fish
Diseases
in Taiwan
B a c t e r i a
B a c t e r i a
 Rickettsia-like organism (RLO)
Rickettsia-like organism (RLO)
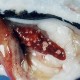
RLO infection in tilapia
In 1992, this new disease appeared and swept across Taiwan. High mortality were seen in tilapia ponds in Kaohsiung and Tainan County, 30%-40% in average and 90% in severe cases. We could not isolate any bacteria from dying fish even we could see numerous bacteria in organ and the circulation. After trying out all the medium formula, Chao used cell culture (TO2, tilapia ovary) and isolate the pathogen successfully. It's an intracellular parasitic organism.Affected fish has skin ulceration, sometimes swollen abdomen and exophthalmia. White spot can be seen in gill filaments in most cases. Spleen swells to 5 - 50 times comparing to normal ones. White focal to diffuse nodules are noted in majorly spleen, and appear in kidney, liver even intestines in severe cases.
Histopathological examination: necrosis in spleen, liver, and kidney. Lots of RLO particles appear in the circulation or are phagocytized by macrophage at early stage of this disease. Then the number of RLO in fish circulation decreases.This organism is different from Piscirickettsia salmonaris isolated from salmonid. We performed PCR with primers designed for detecting Piscirickettsia on these tilapia strains. The amplicon is different in length, indicating divergence between these two organism. Also the host species and temperature are different for these two organisms. The precise nature of tilapia RLO is still left to be studied.