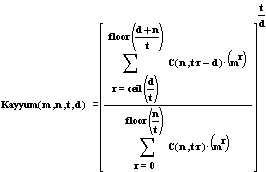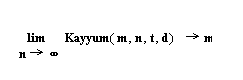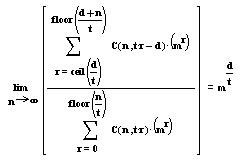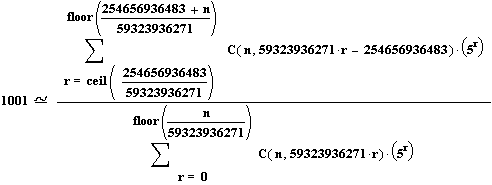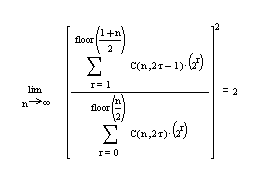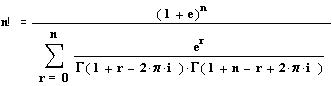return to main page
|
ATTENTION ! May be best
viewed by INTERNET EXPLORER 5.0 or
HIGHER |
THEOREM OF
EL'KAYYUM STATES THAT ;
The function Kayyum(m,n,t,d) ,
(where t , d are any integers
) and
n is an integer going to infinity then the
function , Kayyum(m,n,t,d) --> m
where Kayyum(m,n,t,d) is described
as below.
Binomial coefficient C(x,y) is given by
---> 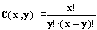
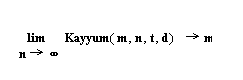 Please click here to see
the related Mathematica program.
as n -->Infinity, Kayyum(m,n,t,d) --> md /
t
Please click here to see
the related Mathematica program.
as n -->Infinity, Kayyum(m,n,t,d) --> md /
t
It is obvious that anybody may play with the summation limits
, since it doesn't make any difference as one of the variables
in the summation limits goes to infinity. But before doing this we
strongly advice to think carefully. Because there is a
reason for these strange limits; as you approximate one or two of the
variables to one or zero , you may lose some of the
correct answers on singular points ; Such as
(d=1 , t=1 , n=1 ) . You will discover some additional singular points as
you exprience more ond more on these functions. After
all , the success of a theorem or a formula depends on the output
that it produces on any odd or singular input that is given to
it.
Some interpretations of the Theorem of
El'kayyum;
A- We may express the
rational power of any real number , by El'kayyum
quite accurately as
following. Please observe the fact that the left hand
side doesn't carry any root terms, but
only power terms which facilitates
the computation and is a rational
number .
But actually , there is no need for n , to go to Infinity.
Quite a high value will suffice for a good
approximation. To compute 78.4534 3 / 7 , (m=78.4534 , d=3 ,
t=7) n=601 ; is enough
for
an accuracy of 25 digits . This
will give ; series ratio computing = 6.485992956804802
stndr. math computing = 6.485992956804799 This accuracy is more than
enough for many calculations.
Please click here
for real values of (m)
Please click here
for complex values of (m)
B-The converse is also true
; we may express any integer number , by El'kayyum
quite accurately as
following.
Express the number 1001 with El'kayyum ratio,
we may write 1001
quite accurately as ;
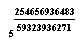 = 1001.000000000000000000118. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
.
= 1001.000000000000000000118. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
.
in here ;
m=5 ,
d=254656936483 , t=59323936271 and
substituting
the values to the formula will yield ;
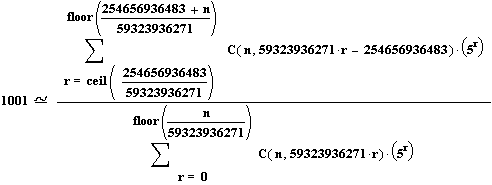 In here, n
should be approximately at least in
the order of 100 times of d or
t. In here, n
should be approximately at least in
the order of 100 times of d or
t. |
Attention ! we think that we may
use this for some purposes (Guess what purposes)
C- Now comes an interesting example
from ancient Pythagoreans .
The left hand side is a ratio of two integers going to
infinity, each
such that ; this ratio gives 2
when squared . Now , does this
remind you of something.
D- A new
theorem to find (n!) by
the relations of e , p , i and the Gamma function. If (e) is eulers constant, i =Ö -1 and , G [f(x)]
stands for Gamma function , then we have the following relation as (n-->¥ ).
Please click here for a
math2.1 tryup for the formula. The right side is a complex number , as (n)
increases the real part of the complex number converges to (n!) ; while the
coefficient of the imaginary part converges to zero. You may extract this
theorem from Euler's famous formula combining (e , p ,
i , -1) and applying the principles relating the theorem of El'Kayyum.
return
to main page
![]()