Way of life
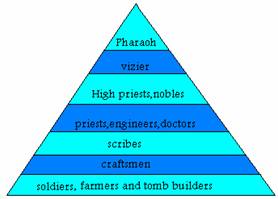 Social classes:
Social classes:
The social
classes were classified in a pyramidal structure according to the professions.
That structure was called the "social pyramid". In the top of that
pyramid was the pharaoh who was not only the ruler of
Society:
The ancient
Egyptian man was the one responsible for his family, he could have more than
one wife. The Egyptian society considered
the man as a hero but it considered the woman spiteful. But on the other hand Egyptian woman shared with the man important legal rights
such as owning lands, operating businesses as well as testifying in
court. She also enjoyed more rights and privileges than the other societies at
that time. This could be traced through the different pictures which showed the
important role of the house wives.

Egyptian Houses:
The lower classes
lived in small villages with narrow streets. They used mud bricks that have
been dried in the sun to build their houses but it didn't last for a long time.
There was a little furniture in those houses which was a bed and small chests
to keep clothes in it. There are different examples for those villages such as El-Amarna and Deir el-Medina.
But
the wealthy people used to live in the countryside or on the outskirts of the
town. They had estates and lived in big houses with high ceiling, pools and
gardens. But those houses also had small furniture such as a low square stool
with a leather seat on it. The chairs were very rare only very wealthy people
had it. The beds were made of woven mat, and small tables were made of wood.
There were also chests which were used to put in it domestic possessions such
as jewelry and clothes.
Garments and jewelries:
The
men and women wore light clothes made of linen due to the hot weather. The men
wore aprons; some of the aprons were above the knee and some were below. And
the women wore long dresses that reached the ankle. The wealthy people wore
sandals made of leather, collars made of
gold and precious stones and pairs of bracelets around the wrist or above the
elbow as well as rings, anklets and earrings. The ordinary people wore
necklaces made of colored pottery beads. The ancient Egyptian women used make
up like the black dye that was used to line their eyes and eyebrows and they
also used perfumes. They also put natural oils on their skin and hair.

Food:
The
Egyptian basic food and drink is bread and beer made from wheet and barley and
the rich people made the wine from their grapes. They were the first people to
make soft light bread and filled with air.
They also were the first to make ovens which they used in baking bread. The ancient Egyptian didn't have sugar, the rich people
used honey to make food sweet while the poor people used dates and fruit
juices. They also liked the strong tasting vegetables like garlic and
onions because they thought that they were useful, and they served the
vegetables with oil and vinegar. They also ate peas and beans. The meat was
expensive so they ate it on occasions. In the ordinary families the housewives
cooked the food, but in rich families they had servants who cooked for them.
![]()